Knee Replacement for Young Patients | Innovative Treatment
Knee replacement for patients under 60 years of age or significantly younger
The decision for a knee replacement in patients under 60 years of age requires careful consideration. Before deciding on a surgical procedure, all non-operative, conservative treatment methods such as physiotherapy, pain therapy, or injections are exhausted.
While knee endoprostheses are traditionally used in older patients with advanced osteoarthritis, the number of knee replacements in younger patients is continuously increasing. According to an analysis by the Bertelsmann Foundation, the number of operations in the age group under 60 years increased by 23 percent between 2013 and 2016.
Challenges: Knee Replacement in Younger Patients
Younger patients place special demands on knee replacements. Their higher activity levels and longer life expectancy can affect the longevity of the implants. The younger the patient is at the time of initial implantation, the higher the probability of one or more revision surgeries during their lifetime, as the average lifespan of a knee replacement is approximately 15 to 20 years.
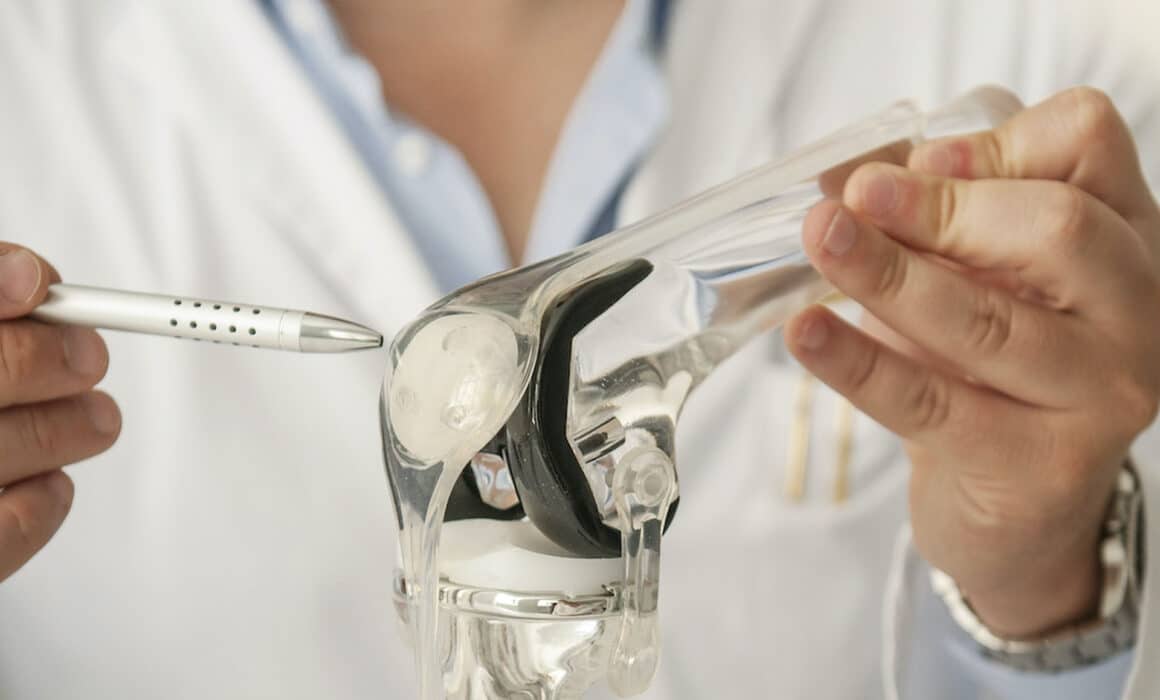
Prosthesis Type: Longevity and Customization
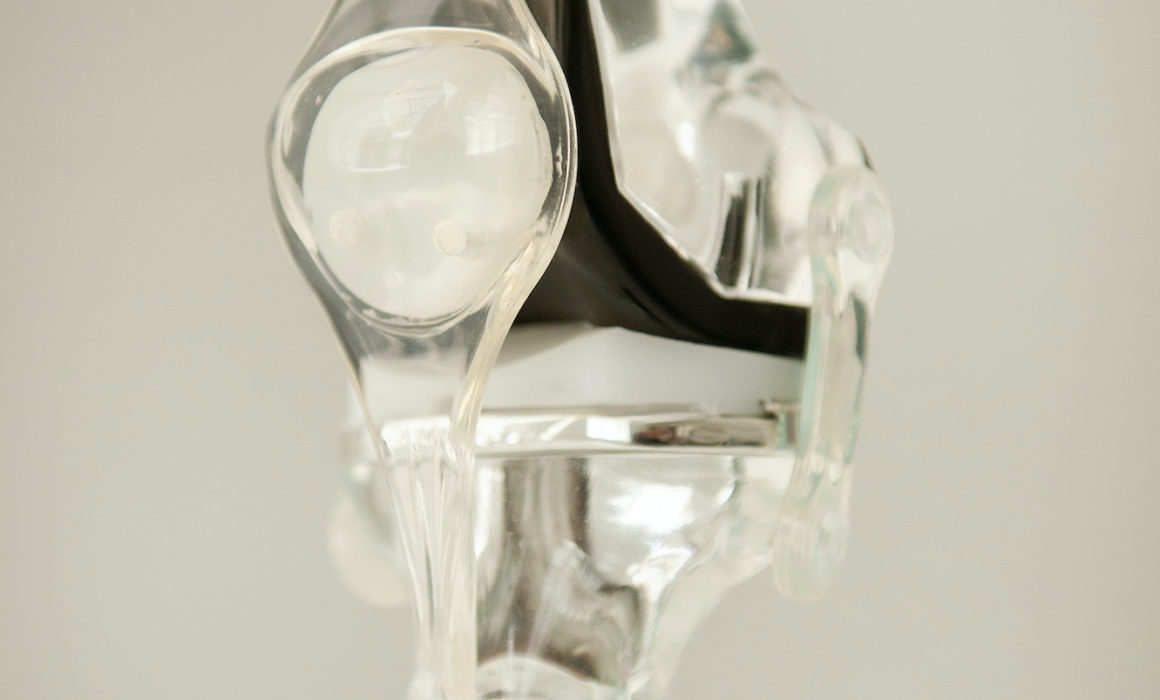
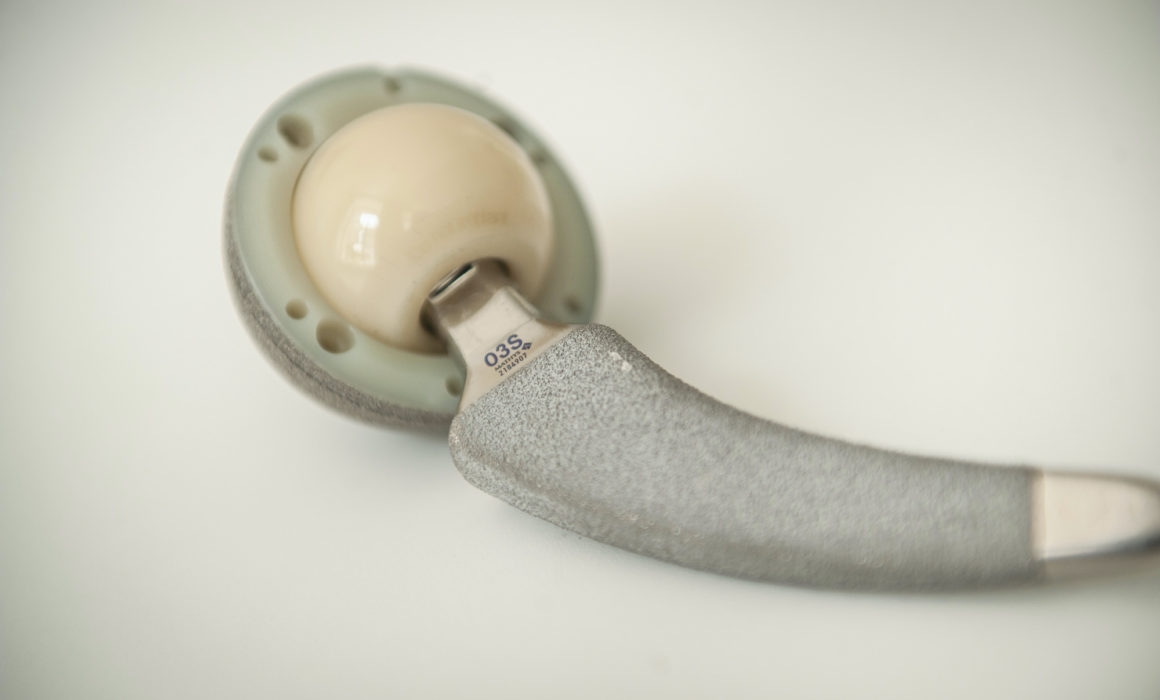
- Longevity: Young patients require prostheses with extended durability. Materials such as highly cross-linked polyethylene, ceramics, or special metal alloys are preferred.
- Customized Prostheses: Custom-made prostheses or those specifically tailored to the patient’s anatomy and lifestyle are often used.
- Partial Prostheses: For limited knee damage, partial prostheses (unicondylar) are often used to preserve healthy structures.
Surgical Technique for Knee Replacement: Precision and Preservation
- Tissue-Sparing Approaches: Minimally invasive techniques and muscle-sparing approaches reduce healing time and improve function.
- Navigated Surgery: Computer-assisted or robot-assisted procedures ensure more precise prosthesis placement, which improves durability.
- Bone-Sparing Procedures: Care is taken to remove as little bone material as possible to facilitate future revision surgeries.
Knee Replacement in Athletically Active Patients: Modern Robot-Assisted Technologies for Precise Procedures
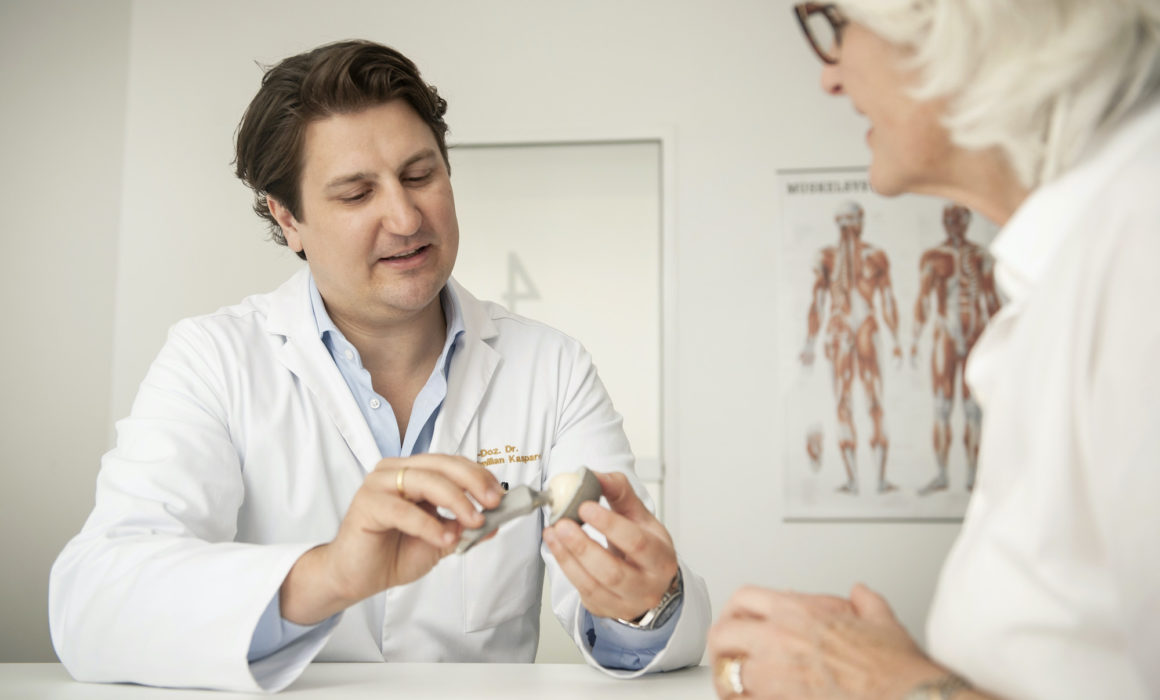
To meet the high demands of young, athletically active patients, Dr. Maximilian Kasparek relies on innovative technologies. Since February 2024, the CORI robotic system has been in use at the Evangelisches Krankenhaus Wien (Evangelical Hospital Vienna), enabling precise adaptation of the prosthesis to the patient’s individual anatomy.
The precision of the robotic system leads to a better fit of the prosthesis, which is particularly advantageous for active patients.
Rehabilitation: Rapid Recovery and Long-Term Care
- More Intensive Rehabilitation: Younger patients have higher demands on knee functionality. Rehabilitation is designed to enable a quick return to daily activities.
- Sports-Related Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy programs are specifically tailored to athletic activities and muscle building.
- Long-Term Care: Regular follow-up examinations are crucial to detect wear or complications early.
Sports After Knee Replacement
A common concern for younger patients is the possibility of returning to sports after surgery. Joint-friendly sports such as swimming, cycling, or golf are recommended, while high-intensity sports with abrupt movements should be avoided. Regular physiotherapy support aids the return to sports and contributes to the longevity of the prosthesis.
Conclusion
The implantation of a knee replacement in patients under 60 years of age requires individual and careful planning. Thanks to modern technologies and customized therapeutic approaches, young, active patients can also regain their quality of life and remain athletically active.
“With the right approach, it is possible to enable young patients to have a high quality of life and engage in sports activities,” emphasizes Dr. Kasparek
For individual consultation and treatment, I am available to you in my private practice in the 18th district of Vienna. Please schedule an appointment to clarify your questions and discuss the best possible therapy.
If you enjoyed this article, you might also be interested in other posts from our blog.